DeepSEA model
In this blog, we will analyze the deep learning model which predict chromatin features using DNA sequence. Using this chromatin features, we can predict the disease.
Introductory Note:
Identifying functional effects of noncoding variants is a major challenge in human genetics. To predict the noncoding-variant effects de novo from sequence, we developed a deep learning–based algorithmic framework, DeepSEA, that directly learns a regulatory sequence code from large-scale chromatin-profiling data, enabling prediction of chromatin effects of sequence alterations with single-nucleotide sensitivity.
DeepSEA:
DeepSEA model takes DNA sequence as input and predict the chromatin features. In total, we will predict 919 chromatin features. Thereby we will be able to predict the effects of sequence on chromatin which in turn can be used for prediction of disease.
Model planning:
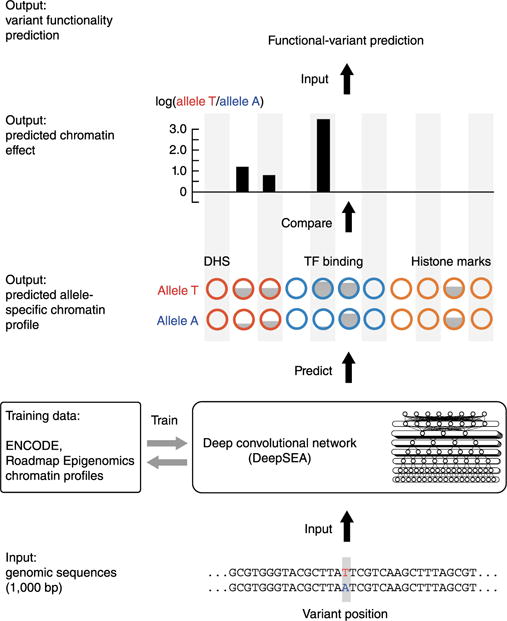
Input:
DeepSEA model takes 1000bp DNA sequence as input. DNA sequence consist of A, T, G and C nucleotides. A is represented as [1, 0, 0, 0], T is represented as [0, 1, 0, 0], G is represented as [0, 0, 1, 0] and C is represented as [0, 0, 0, 1]. Input is given to the modle in such format.
Architecture:
The deep convolutional network model features sequential alternating convolution and pooling layers that extract sequence features at different spatial scales, followed by one fully connected layer that integrates information from the full-length sequence and a sigmoid output layer that computes probability output for each individual chromatin factor feature. Each layer of the deep convolutional network executes a linear transformation of the output from the previous layer by multiplying a weight matrix, followed by a nonlinear transformation. The weight matrix is learned during training to minimize predictive errors.
The following model architecture is used in DeepSEA model:
Model Architecture:
- Convolution layer ( 320 kernels. Window size: 8. Step size: 1. )
- Pooling layer ( Window size: 4. Step size: 4. )
- Convolution layer ( 480 kernels. Window size: 8. Step size: 1. )
- Pooling layer ( Window size: 4. Step size: 4. )
- Convolution layer ( 960 kernels. Window size: 8. Step size: 1. )
- Fully connected layer ( 925 neurons )
- Sigmoid output layer
Regularization Parameters: Dropout proportion (proportion of outputs randomly set to 0):
- Layer 2: 20%
- Layer 4: 20%
- Layer 5: 50%
- All other layers: 0%
Training the Model:
To train the model, we minimized the objective function, which is defined as the sum of negative log likelihood (NLL) and regularization terms for controlling overfitting. Specifically,
where s indicates index of training samples and t indicates index of chromatin features. indicates 0,1 label for sample s, chromatin feature t. represents the predicted probability output of the model for chromatin feature t given input . We used a combination of multiple regularization techniques typical for training deep neural networks. L2 regularization term is defined to be the sum of squares of all the weight matrix entries. is defined to be the L1 norm of all the output values of the last layer (fully connected layer) before the output layer. Additionally, the optimization is subjected to regularization constraints that for any layer m and neuron n, or the L2 norm of weights for any neuron must not be larger than a specified value. The values of , and are as follow:
- L2 regularization (): 5e-07
- L1 sparsity (): 1e-08
- Max kernel norm (): 0.9
Summary:
So using this model we can predict the chromatin features using DNA sequence which we can later use in prediction of disease.